Use Excel as your calculator
Instead of using a calculator, use Microsoft Excel to do the math!
You can enter simple formulas to add, divide, multiply, and subtract two or more numeric values. Or use the AutoSum feature to quickly total a series of values without entering them manually in a formula. After you create a formula, you can copy it into adjacent cells — no need to create the same formula over and over again.
Subtract in Excel

Multiply in Excel

Divide in Excel

Learn more about simple formulas
All formula entries begin with an equal sign (=). For simple formulas, simply type the equal sign followed by the numeric values that you want to calculate and the math operators that you want to use — the plus sign (+) to add, the minus sign (-) to subtract, the asterisk (*) to multiply, and the forward slash (/) to divide. Then, press ENTER, and Excel instantly calculates and displays the result of the formula.
For example, when you type =12.99+16.99 in cell C5 and press ENTER, Excel calculates the result and displays 29.98 in that cell.
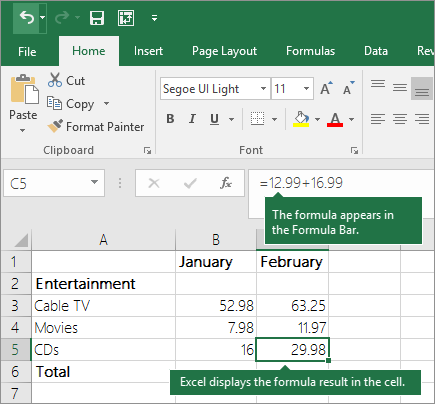
The formula that you enter in a cell remains visible in the formula bar, and you can see it whenever that cell is selected.
Important: Although there is a SUM function, there is no SUBTRACT function. Instead, use the minus (-) operator in a formula; for example, =8-3+2-4+12. Or, you can use a minus sign to convert a number to its negative value in the SUM function; for example, the formula =SUM(12,5,-3,8,-4) uses the SUM function to add 12, 5, subtract 3, add 8, and subtract 4, in that order.
Use AutoSum
The easiest way to add a SUM formula to your worksheet is to use AutoSum. Select an empty cell directly above or below the range that you want to sum, and on the Home or Formula tabs of the ribbon, click AutoSum > Sum. AutoSum will automatically sense the range to be summed and build the formula for you. This also works horizontally if you select a cell to the left or right of the range that you need to sum.
Note: AutoSum does not work on non-contiguous ranges.
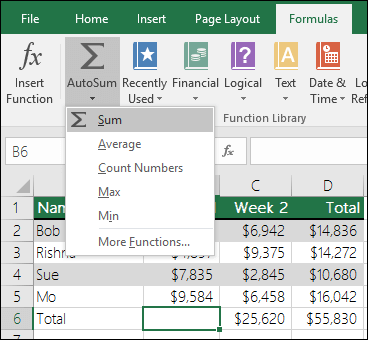
AutoSum vertically
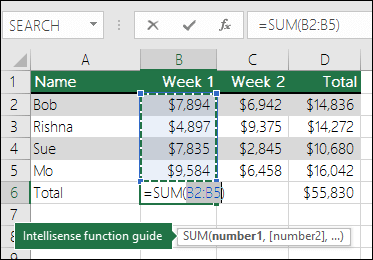
In the figure above, the AutoSum feature is seen to automatically detect cells B2:B5 as the range to sum. All you need to do is press ENTER to confirm it. If you need to add/exclude more cells, you can hold the Shift Key + the arrow key of your choice until your selection matches what you want. Then press Enter to complete the task.
Intellisense function guide: the SUM(number1,[number2], …) floating tag beneath the function is its Intellisense guide. If you click the SUM or function name, it will change o a blue hyperlink to the Help topic for that function. If you click the individual function elements, their representative pieces in the formula will be highlighted. In this case, only B2:B5 would be highlighted, since there is only one number reference in this formula. The Intellisense tag will appear for any function.
AutoSum horizontally

Learn more in the article on the SUM function.
Avoid rewriting the same formula
After you create a formula, you can copy it to other cells — no need to rewrite the same formula. You can either copy the formula, or use the fill handle
For example, when you copy the formula in cell B6 to C6, the formula in that cell automatically changes to update to cell references in column C.
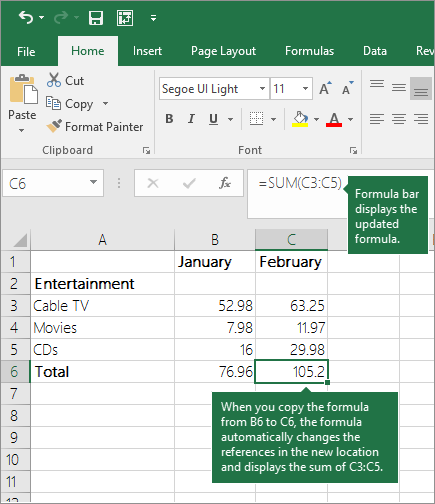
When you copy the formula, ensure that the cell references are correct. Cell references may change if they have relative references. For more information, see Copy and paste a formula to another cell or worksheet.
What can I use in a formula to mimic calculator keys?
|
Calculator key |
Excel method |
Description, example |
Result |
|
+ (Plus key) |
+ (plus) |
Use in a formula to add numbers. Example: =4+6+2 |
12 |
|
- (Minus key) |
- (minus) |
Use in a formula to subtract numbers or to signify a negative number. Example: =18-12 Example: =24*-5 (24 times negative 5) |
-120 |
|
x (Multiply key) |
* (asterisk; also called "star") |
Use in a formula to multiply numbers. Example: =8*3 |
24 |
|
÷ (Divide key) |
/ (forward slash) |
Use in a formula to divide one number by another. Example: =45/5 |
9 |
|
% (Percent key) |
% (percent) |
Use in a formula with * to multiply by a percent. Example: =15%*20 |
3 |
|
√ (square root) |
SQRT (function) |
Use the SQRT function in a formula to find the square root of a number. Example: =SQRT(64) |
8 |
|
1/x (reciprocal) |
=1/n |
Use =1/n in a formula, where n is the number you want to divide 1 by. Example: =1/8 |
0.125 |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in Communities.











