This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the NOMINAL function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the nominal annual interest rate, given the effective rate and the number of compounding periods per year.
Syntax
NOMINAL(effect_rate, npery)
The NOMINAL function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Effect_rate Required. The effective interest rate.
-
Npery Required. The number of compounding periods per year.
Remarks
-
Npery is truncated to an integer.
-
If either argument is nonnumeric, NOMINAL returns the #VALUE! error value.
-
If effect_rate ≤ 0 or if npery < 1, NOMINAL returns the #NUM! error value.
-
NOMINAL (effect_rate,npery) is related to EFFECT(nominal_rate,npery) through effective_rate=(1+(nominal_rate/npery))*npery -1.
-
The relationship between NOMINAL and EFFECT is shown in the following equation:
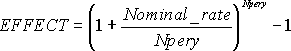
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Data |
Description |
|
|
0.053543 |
Effective interest rate |
|
|
4 |
Number of compounding periods per year |
|
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=NOMINAL(A2,A3) |
Nominal interest rate with the terms above |
0.05250032 |










